Home > Skills > Merit Badges > Digital Resource Guides > Aviation > MB – Aviation – 1.C
Merit Badges > Digital Resource Guides > Aviation > 1.C


Aviation Merit Badge
Explain the difference between a fixed-wing and a rotary-wing aircraft, and the benefits of each.
Here’s an easy way to understand the difference between fixed-wing and rotary-wing aircraft:
Fixed-Wing Aircraft
Definition: These are the types of aircraft that have stationary wings. The wings are attached to the main body (fuselage) of the aircraft and do not move.
How they fly: Fixed-wing aircraft rely on the forward motion of the aircraft to generate lift. The engines (often jet engines or propellers) push the plane forward, and the wings create upward force as air flows over and under them. The faster the plane moves, the more lift is generated.

Examples: Cessna 172 private aircraft, Boeing 747 passenger jet airplane, F-15 “Eagle” military fighter jet.
Advantages: They’re generally faster and more efficient for long-distance travel. They can carry more passengers or cargo.
Disadvantages: Fixed-wing aircraft need a runway to take off and land, so they can’t hover or land vertically.

Rotary-Wing Aircraft
Definition: These aircraft have rotating blades (called rotors) instead of fixed wings. The rotor blades spin around a central hub, generating lift and thrust.
How they fly: The rotor blades create lift by spinning rapidly through the air. This allows rotary-wing aircraft to hover in place, fly vertically, or move in any direction (up, down, forward, backward, side-to-side). The main rotor provides lift, while a tail rotor often helps control the direction of the aircraft.
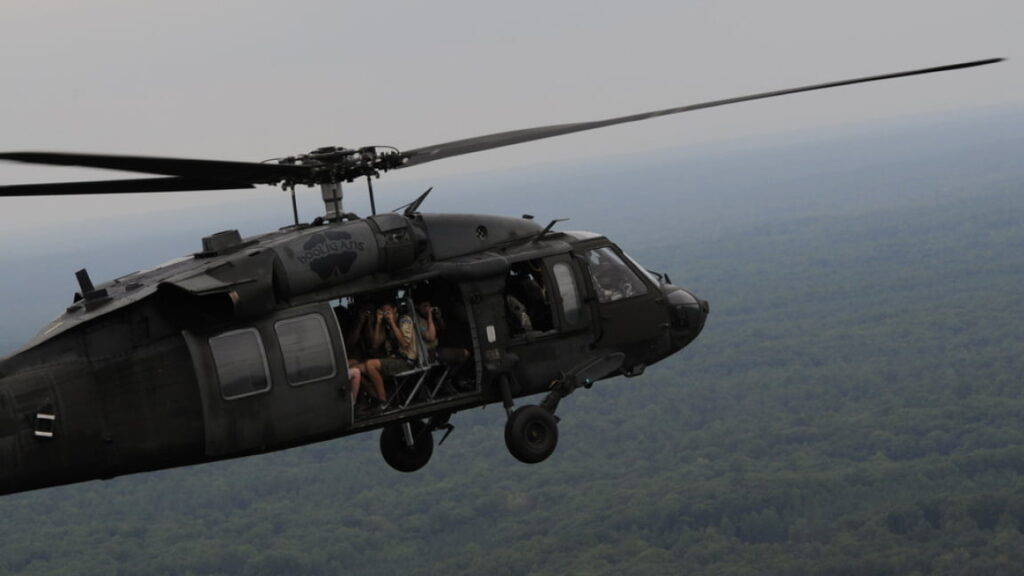

Examples: Bell 206 Jet Ranger, Robinson R44 Ranger, Sikorsky UH-60 “Black Hawk” military helicopter.
Advantages: They can hover in place and can take off and land vertically, meaning they don’t need a runway. This makes them useful for rescue missions, military operations, and places where a runway isn’t available.
Disadvantages: They are usually slower and less fuel-efficient than fixed-wing aircraft. They also have more moving parts, which can increase maintenance.

Key Differences

Fixed wing aircraft are generally easier to fly and service; rotary wings are more complex and challenging to operate.

Fixed-wing aircraft need a runway to take off and land, while rotary-wing aircraft can take off and land vertically (no runway needed).
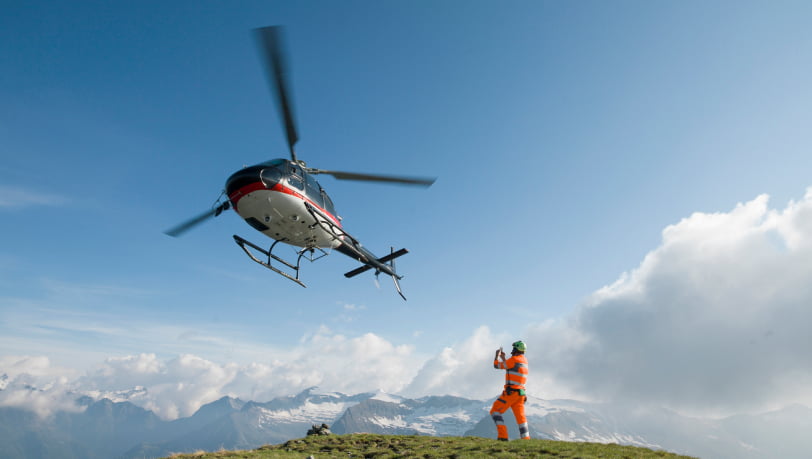

Fixed-wing aircraft are generally faster and more fuel-efficient over long distances. Rotary-wing aircraft are more maneuverable but are usually slower and less efficient.

Both fixed wing and rotary wing aircraft offer their own unique advantages (and challenges) – pilots should select the right aircraft for their specific needs to get the job done right!

Both fixed wing and rotary wing aircraft offer their own unique advantages (and challenges) – pilots should select the right aircraft for their specific needs to get the job done right!
See the difference in action!
Now you know the primary methods that an aircraft uses to fly. Do you know how these aircraft get their power?